
What are the different impacts of the vegetable protein versus animal protein, and the benefits of plant proteins translate into plant protein insulation?
Are they healthy or non -hamburgers based on plants? The answer is: In comparison to what? Eating is a kind of zero sum game where each meal has an opportunity cost. Every time we get something in our mouths, it is a lost opportunity to eat something even more healthy. So, if we want to know if something is healthy, we have to compare it with what we would be eating. For example, are eggs healthy? In comparison with a breakfast sausage link, yes, but compared to oatmeal? Not even close. The sausage is considered A carcinogen of group 1. We know that the consumption of processed meat causes cancer. Every 50 grams that serves up to date (equal to approximately one or two breakfast sausages) has been related to a higher 18 percent risk of colorectal cancer. In fact, the risk that colorectal cancer will eat these daily sausages is almost the same as the greatest risk of lung cancer from which we would get breathing In second hand, cigarette smoke living with a smoker. Then, compared to the sausage, the eggs are healthy, but compared to oatmeal, the eggs are not.
When arrives Beyond the flesh and impossible foods of plant -based hamburgers, they can be better because they have less saturated fats than conventional meat burgers, but if you really want less saturated fats, plants based on plants are not rival for unprocessed plant foods, such as lentils and beans. And the lentil soup or a bean burrito could certainly fill the same culinary niche as a hamburger at lunchtime. But, if you are going to have some kind of hamburger, it is easy to argue that plants -based versions are healthier, as seen below already 1:43 in my video Plant -based protein: Are those isolated from peas and soy proteins harmful?.
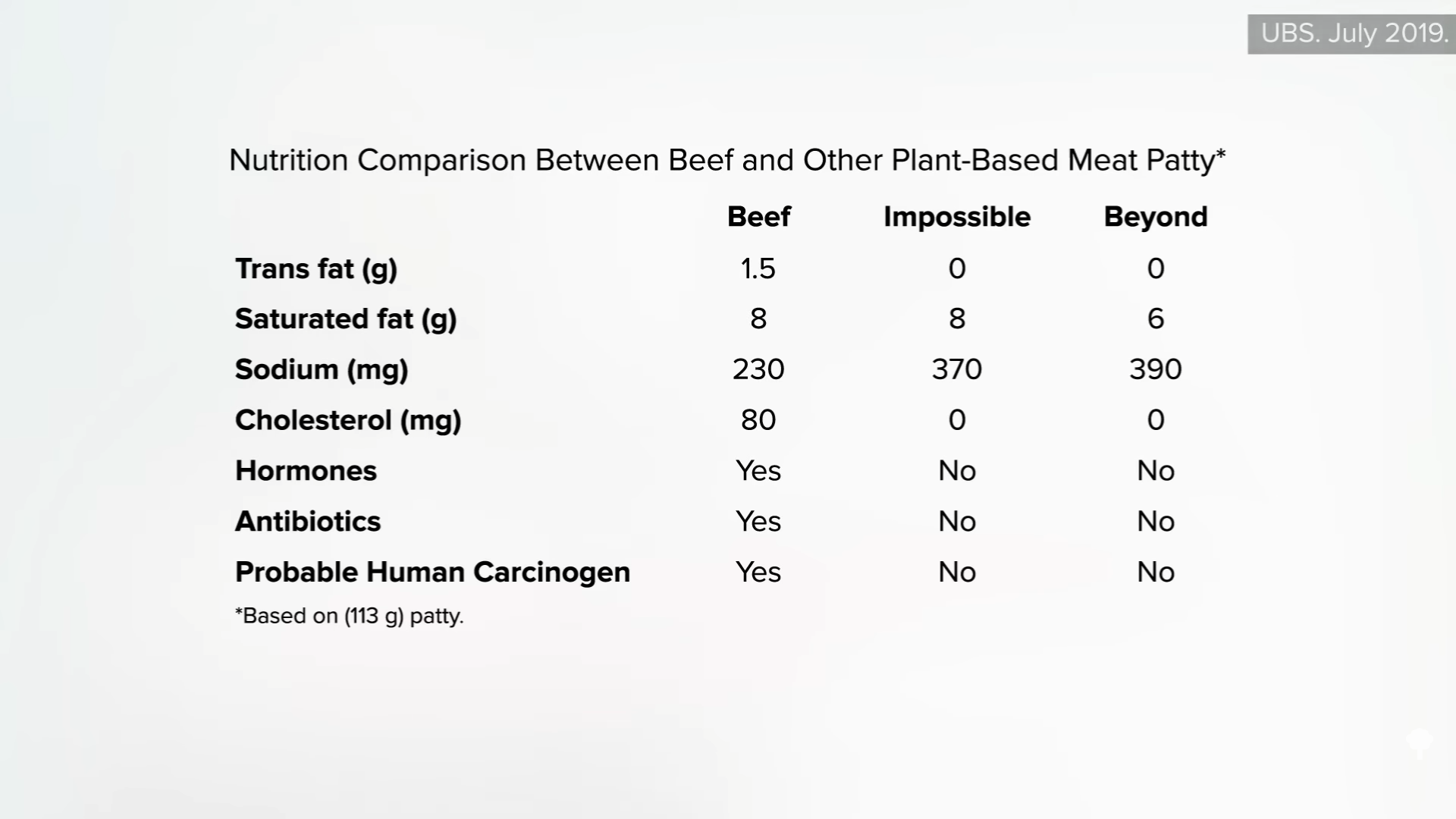
There is However, a sodium problem with those plants based empanadas, and are not much lower in saturated fats. That is Due to coconut oil, which is as bad as animal fat, so there are it’s not A lot of advantage in that front. I’m excited to say that Beyond meat Since then, it has significantly improved its formula since I made that graph for UBS. Now beyond has 310 mg of sodium and only 2 grams of saturated fat thanks to a change of coconut oil to avocado oil.
Total protein is similar in all areas. Does that matter? Is there any advantage to eat plants proteins over animals? Come on look in the association between intake and mortality of plant and animal proteins. In Harvard’s twin cohorts, which followed more than 100,000 men and women for decades, the researchers wrote: «After adjusting for other dietary and lifestyle factors, the intake of animal proteins was associated with a higher risk of mortality, particularly the mortality of CVD», that is, to die of cardiovascular disease, «the one that was associated with a higher protein intake The lowest mortality of mortality by all houses «, which means that it is a lower risk of dying of the cause of the cause of the cause of all causes of the cause. Then, «replace the animal protein of several origins with the plant protein was associated with lower mortality,» especially if processed meat and egg protein were replaced, since they were the worst.
When it comes to living a longer life, vegetable protein sources exceed each and every one of the animal protein sources. Not only better than bacon and eggs, but better than hamburgers, chicken, turkey, fish and dairy protein, as shown here and 2:53 in my video.
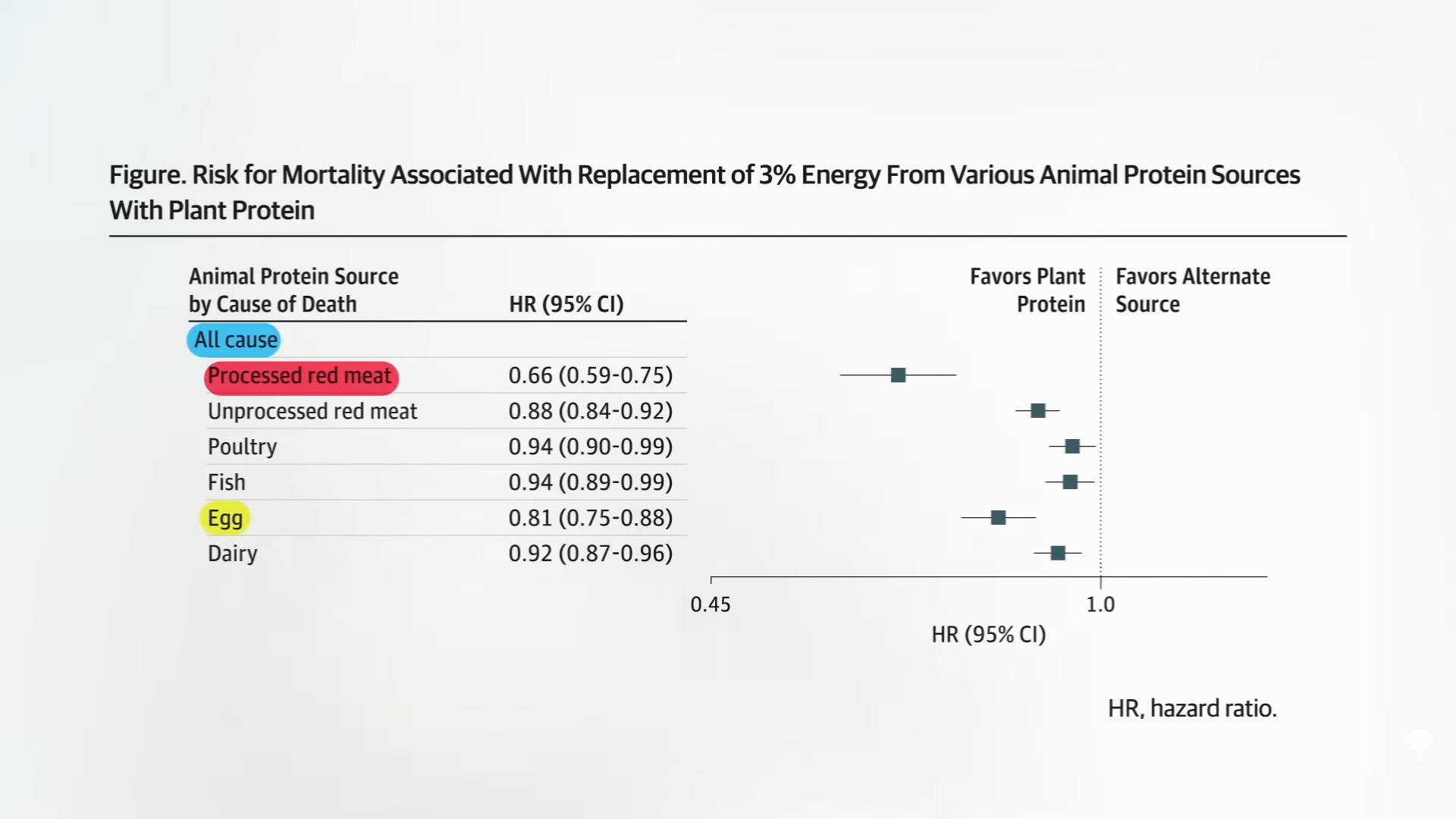
Together with other studies, these «findings support The importance of protein sources for long-term health outcome and suggests that plants constitute a preferred protein source compared to animal foods. «Why? Well? is Similar to animal protein that, at dose high enough, such as eating two burgers impossible per day, our IGF-1 can get a lump. But the only reason we care about IGF-1 is the risk of cancer and, in any case, «a greater soy intake is associated with a decrease in the risk of breast and prostate cancer.»
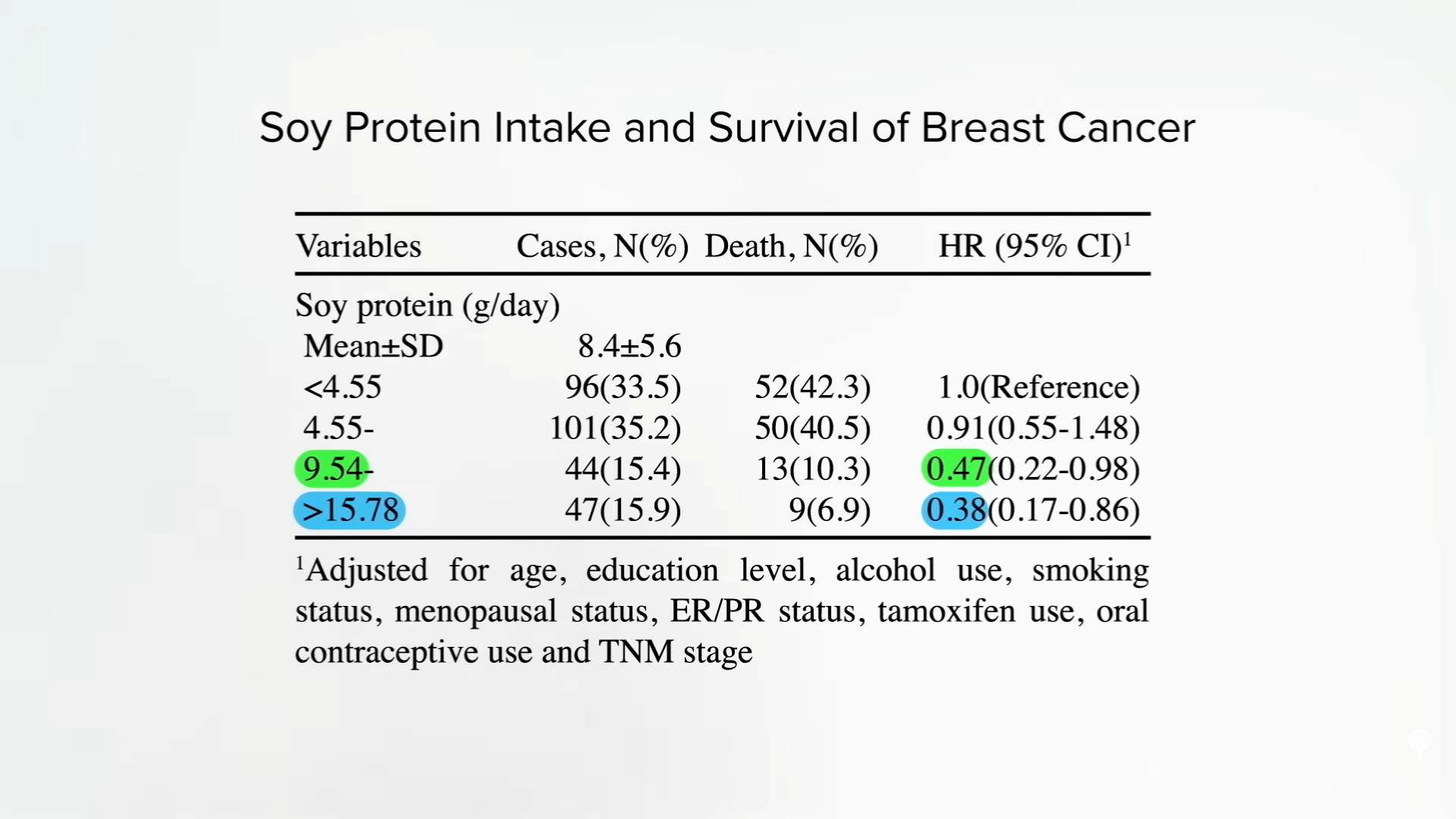
A recent systematic review and a meta -analysis found This «soy protein intake was associated with a decrease in risk in breast cancer mortality,» for example. «A 12% reduction in the death of breast cancer was observed for each 5-g/day increase in soy protein intake.» But, as shown below and 4:07 in my videoHigh level groups in these studies were In the order of more than 16 grams a day, which was associated with an incredible risk 62 percent of dying of breast cancer. More than 10 grams of soy protein daily can be good, associated with almost half reduce the risk of breast cancer mortality, and obtain more than 16 grams a day can be better, which is like an impossible hamburger per day. (We just don’t know what happens at consumption levels well above that).
Vegetable protein has also been » bound To reduce blood pressure, reduced low density lipoprotein [LDL cholesterol] levels and better insulin sensitivity. The replacement of the vegetable protein with animal protein has been related to a lower incidence of ECV [cardiovascular disease] and type 2 diabetes. In fact, 21 different studies following Almost half a million people found that «high … animal protein intakes are associated with a higher risk of DM2 [type 2 diabetes]while moderate intake of vegetable proteins is associated with a decrease in the risk of DM2 ”. However, those were only observation studies. The researchers tried to control other dietary and lifestyle factors, but the cause and effect cannot be tested until it is tested.
Enter «effect of Replacement Animal protein with vegetable protein in glycemic [Blood Sugar] Diabetes control: a systematic review and a meta -analysis of random controlled trials. «The researchers found that replacing only around one third of protein from animal sources with plant sources showed significant improvements in the control of long -term blood sugar, the blood sugar in fasting and insulin blood.
The same with cholesterol. A systematic review and a meta -analysis of random controlled tests on the effect of plant protein on blood fats again found which replacing animal protein with vegetable protein decreases LDL cholesterol. In addition, this benefit occurs if it begins with high or low cholesterol, if you are replacing dairy, meat and eggs, and if you are changing in soybeans or other vegetable proteins, as seen here and 5:31 in my video.
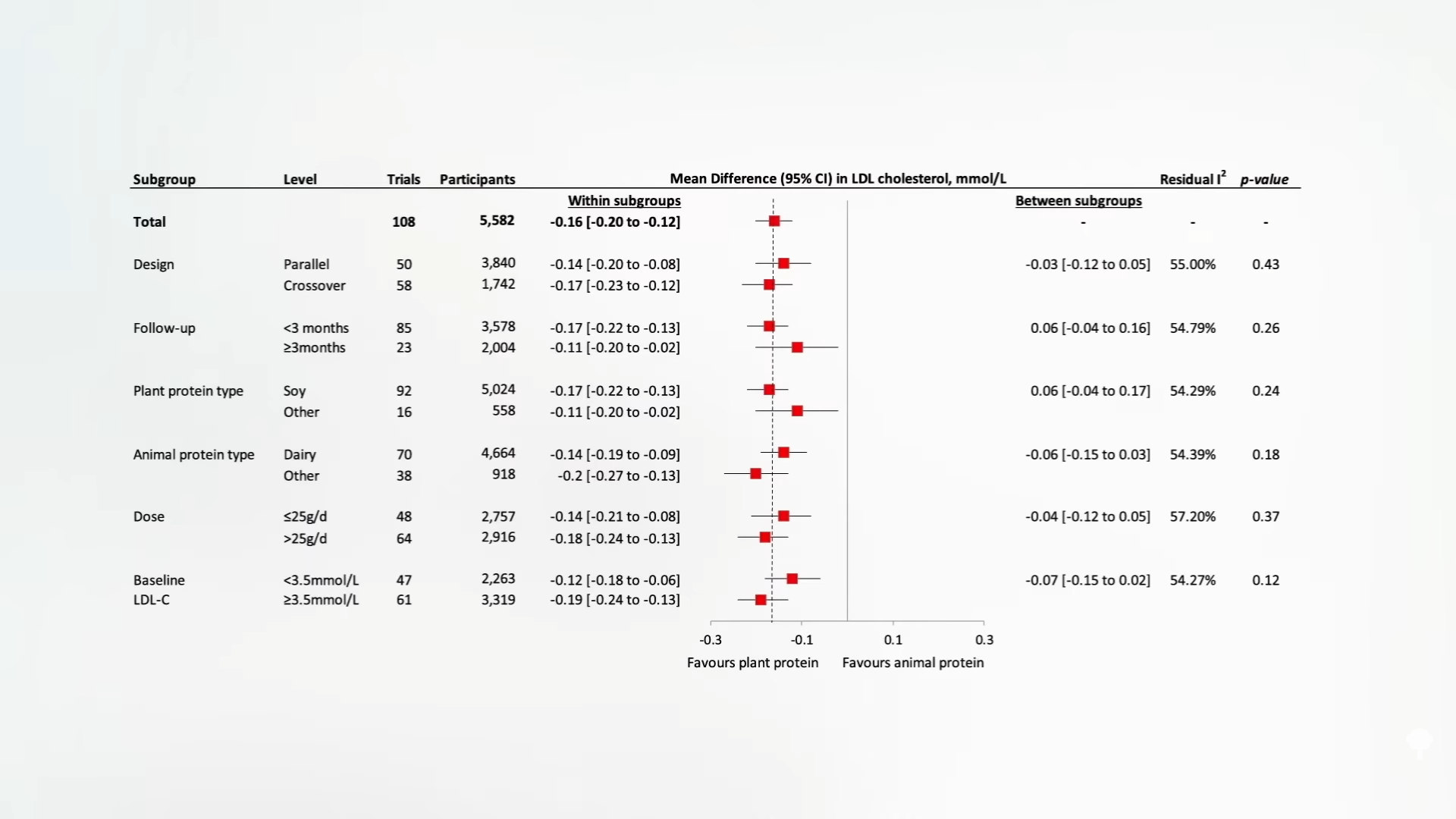
Have acquaintance On the beneficial effects of soybeans on cholesterol for almost 40 years, but other sources of plant protein can also be useful. However, in the case of hamburgers based on plants such as Beyond Beef and The Impossible Burger, meat is not being replaced by beans. These products are mostly isolated vegetable proteins, mainly isolated from pea proteins in Beyond meat concentrated soybean products and protein Impossible foods products. If they areolate vegetable proteins in themselves, will they still get benefits? Surprisingly, yes. Check out a look.
The researchers concluded: «Interestingly, ours … the analysis did not find a significant difference between protein insulation products and entire food sources for any given end point, suggesting that the reducing cholesterol effects are at least, partly, attributable to plant protein itself instead of only associated nutrients.» So, it is not just because the vegetable protein travels with fiber or less saturated fats. Vegetable proteins break down in a different distribution of amino acids. So, if you give arginine people, an amino acid that is more in plant foods, which can only tear down cholesterol, for example. And the vegetable protein concentrates used in these meatless products No only pure protein; They retain some active compounds, such as phytosterols and antioxidants, which can also have beneficial effects.
This is the third of a series on plants based meats. If you missed the first two, look Environmental impacts of plant -based meat substitutes and Are meat and hamburger healthy healthy?.
See the publications related below to watch the next videos about plants based.






